最近在学习 APUE,所以顺便将每日所学记录下来,一方面为了巩固学习的知识,另一方面也为同样在学习APUE的童鞋们提供一份参考。
本系列博文均根据学习《UNIX环境高级编程》一书总结而来;
运行环境:
操作系统: ubutnu 16.04
编译器:QtCreator CLion 2020.3
基础知识 unix体系结构 从严格意义来说,可将操作系统定义为一种软件,它控制计算机硬件资源,提供程序运行环境。我们通常将这种软件成为内核(kernel),内核的结构被称为系统调用 。公用函数库建立在系统调用接口之上,应用程序既可以使用公用函数库,也可以使用系统调用;
登录 shell 用户登录后,系统会显示一些系统信息,然后我们可以向shell输入命令。
shell的用户输入通常来自于终端(交互式shell),有时来自文件。
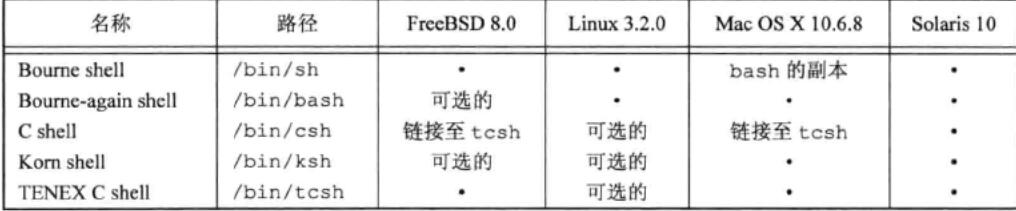
文件和目录 文件系统 UNIX文件系统是目录和文件的一种层次结构,所有文件的起点是根目录,这个目录是”/“;
目录是一个包含目录项的文件,在逻辑上,可以认为每个目录项都包含一个文件;
文件名 目录中的各个文件成为文件名。
路径名 由斜线分割的一个或多个文件名组成的序列构成路径名,以斜线开头的路径成为绝对路径名;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include "my_err.h" #include <dirent.h> int main (int argc, char *argv[]) DIR *dp; struct dirent *dirp ; if (argc != 2 ) err_quit("usage: %s directory_name" , argv[0 ]); if ((dp = opendir(argv[1 ])) == NULL ) err_sys("can't open %s" , argv[1 ]); while ((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL ) printf ("%s\n" , dirp->d_name); closedir(dp); return 0 ; }
输入和输出 文件描述符 文件描述符通常是一个小的非负整数,内核用以标识一个特定进程正在访问的文件。当内核打开一个现有文件描述符或创建一个文件时,它都会返回一个文件描述;
标准输入、标准输出和标准出错
标准输入 STDIN_FILENO 0
标准输出 STDOUT_FILENO 1
标准出错 STDERR_FILENO 2
不带缓冲的I|O 函数open、read、write、lseek和close提供了不带缓冲的I/O;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include "my_err.h" #define BUFFSIZE 4096 int main (void ) int n; char buf[BUFFSIZE]; while ((n = read(STDIN_FILENO,buf,BUFFSIZE)) > 0 ) { if (write(STDOUT_FILENO,buf,n) != n) { err_sys("write error" ); } } if (n < 0 ) { err_sys("read error" ); } exit (0 ); }
标准I/O 标准I/O函数为那些不带缓冲的函数提供了一个带缓冲的接口;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include "my_err.h" int main (void ) int c; while ((c = getc(stdin )) != EOF) { if (putc(c,stdout ) == EOF) { err_sys("output error" ); } } if (ferror(stdin )) { err_sys("input error" ); } exit (0 ); }
程序和进程 进程和进程ID 程序的执行实例被成为进程(process),unix系统确保每个进程都拥有一个唯一的数字标识符,成为进程ID;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include "my_err.h" #include <time.h> int main (void ) printf ("hello world form process ID %ld\n" ,(long )getpid()); printf ("hello world form process ID %ld\n" ,(long )getppid()); sleep(100 ); exit (0 ); }
使用getpid得到进程的ID,使用getppid得到父进程的ID;
进程控制 有三个函数用于进程控制得到主要函数:fork、exec、waitpid;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include <sys/wait.h> #include "my_err.h" int main (void ) char buf[MAXLINE]; pid_t pid; int status; printf ("%% " ); while (fgets(buf,MAXLINE,stdin ) != NULL ) { if (buf[strlen (buf) - 1 ] == '\n' ) { buf[strlen (buf) - 1 ] = 0 ; } if ((pid = fork()) < 0 ) { err_sys("fork error" ); } else if (pid == 0 ) { execlp(buf,buf,(char *)0 ); err_ret("couldn't execute: %s" ,buf); exit (127 ); } if ((pid = waitpid(pid,&status,0 )) < 0 ) { err_sys("waitpid error" ); } printf ("%% " ); } exit (0 ); return 0 ; }
线程和线程ID 通常一个进程只有一个控制线程在某一时刻执行一组机器指令。一个进程内的所有线程共享同一地址空间、文件描述符、栈以及与进程相关的属性。
出错处理 linux定义两个函数,它们用于输出出错信息;
1 2 3 4 #include <string.h> #include <stdio.h> char *strerror (int errnum) void perror (cosnt char *msg)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include <sys/wait.h> #include <errno.h> #include <string.h> int main (int argc,char *argv[]) fprintf (stderr ,"EACCESS: %s\n" ,strerror(EACCES)); errno = ENOENT; perror(argv[0 ]); exit (0 ); }
用户标识 用户ID 口令文件登录项中的用户(ID)是一个整形值,它向系统标识各个不同的用户;
用户ID为0的用户为根用户(root)或超级用户(superuser)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #include "../../include/apue.h" int main (void ) printf ("uid = %d,gid = %d\n" ,getuid(),getgid()); exit (0 ); }
信号 信号用于通知进程发生了某种情况。进程有以下三种处理信号的方式:
忽略信号。有些信号标识硬件异常,因为这些异常产生的后果不确认,所以不推荐;
按系统默认方式处理。对于除数为0,系统默认方式是终止该进程;
提供一个函数,信号发生时调用该函数,这被称为捕捉该信号;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 #include "../../include/apue.h" #include <sys/wait.h> #include "my_err.h" static void sig_int (int ) int main (void ) char buf[MAXLINE]; pid_t pid; int status; if (signal(SIGINT,sig_int) == SIG_ERR) { err_sys("signal error" ); } printf ("%% " ); while (fgets(buf,MAXLINE,stdin ) != NULL ) { if (buf[strlen (buf) - 1 ] == '\n' ) { buf[strlen (buf) - 1 ] = 0 ; } if ((pid = fork()) < 0 ) { err_sys("fork error" ); } else if (pid == 0 ) { execlp(buf,buf,(char *)0 ); err_ret("couldn't execute: %s" ,buf); exit (127 ); } if ((pid == waitpid(pid,&status,0 )) < 0 ) { err_sys("waitpid error" ); } printf ("%% " ); } exit (0 ); } void sig_int (int signo) printf ("interrupt\n%% " ); }
时间值 1 2 3 4 time msfconsole real 0m11.239s //时钟时间 user 0m4.531s //用户CPU时间 sys 0m2.803s //系统CPU时间